How Underground Power Lines Are Installed and Maintained
Underground power lines are electrical cables buried beneath the ground to provide power to residential, commercial, and industrial areas. Their importance is growing due to the need for reliable and aesthetically pleasing power solutions. Understanding the installation and maintenance of these lines is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
This article will cover:
- The process of underground power line installation
- The benefits and challenges associated with these lines
- Maintenance practices necessary for their longevity
- Safety measures to consider when dealing with underground power lines
By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how underground power lines are installed and maintained, including insights into the benefits they offer and the challenges they present. If you have any further questions or need assistance regarding underground power line services, feel free to contact us for more information.
Understanding Underground Power Lines
Underground power lines are a type of electrical infrastructure where cables are buried beneath the ground instead of being suspended on poles. This approach contrasts with overhead power lines, which remain visible and exposed to the elements. When comparing power line types, underground systems offer a solution that prioritizes both safety and appearance.
Common Uses:
- Residential: Frequently used in new housing estates to preserve neighborhood aesthetics and reduce safety concerns.
- Commercial: Shopping centers, business parks, and hospitals often rely on underground cabling for uninterrupted service.
- Industrial: Factories and large facilities use buried lines to protect critical operations from external hazards.
Benefits of Underground Power Lines:
- Protection from Weather: Shielded from wind, storms, bushfires, and accidental vehicle contact—key factors in reducing outages.
- Improved Aesthetics: Eliminates visual clutter, maintaining clean streetscapes and property values.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces risks of electrocution or falling wires, addressing safety considerations for both workers and the public.
“With underground cabling, you gain reliability without sacrificing the look or safety of your property.”
Selecting between overhead and underground options depends on specific project needs. The advantages of underground installations stand out most in areas where resilience, visual appeal, and public safety are priorities.
The Installation Process Explained
Step-by-Step Overview of Installation
1. Planning
- Initial site survey and assessment.
- Detailed planning including obtaining necessary permits and approvals.
- Coordination with local utilities to identify existing underground services.
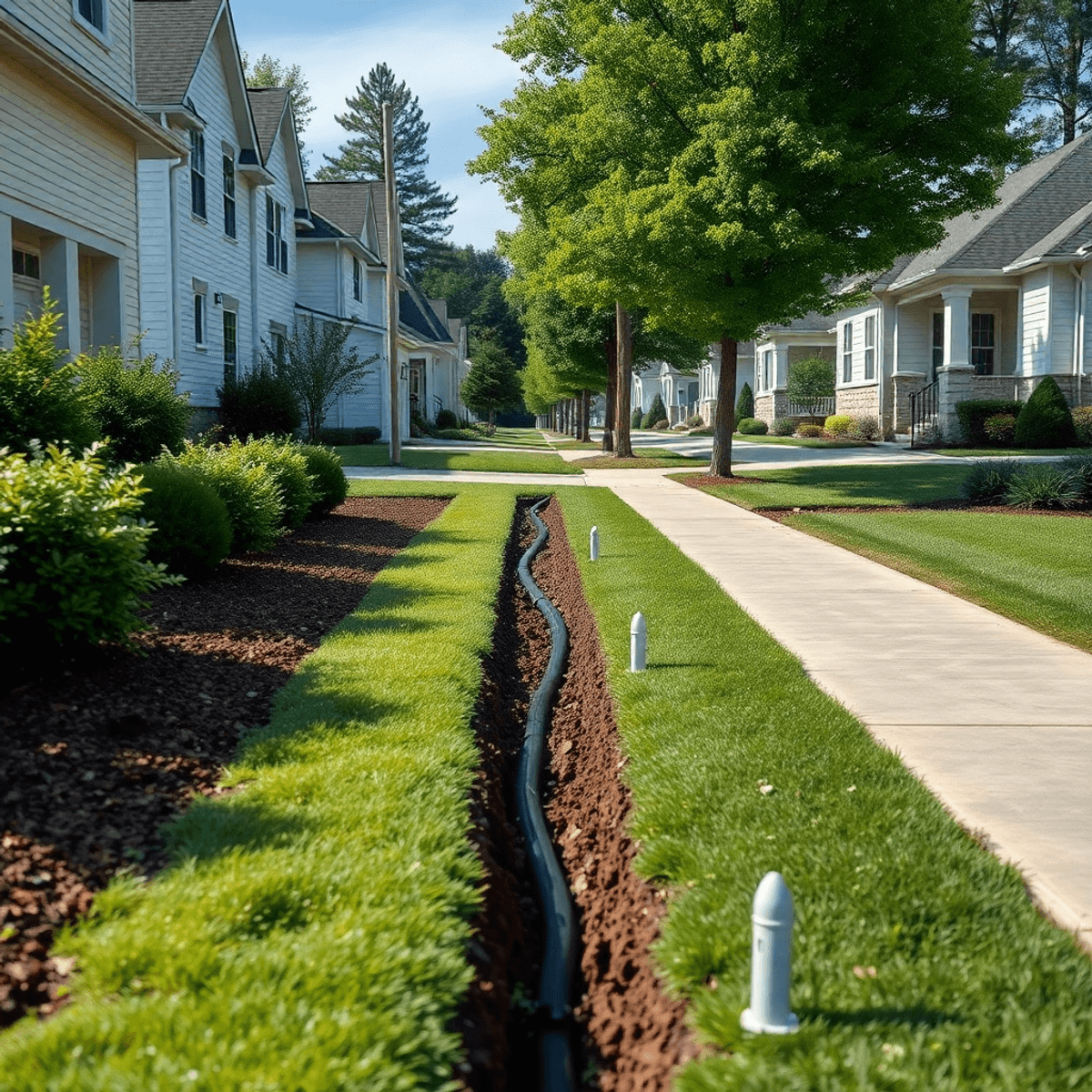
2. Trench Digging
- Use of trenching equipment to dig precise trenches.
- Typical residential depth requirement: 18-24 inches to ensure adequate protection and accessibility.
3. Cable Laying
Two primary methods: direct burial or conduit installation.
- Direct Burial: Cables are laid directly into the trench, usually encased in a protective covering.
- Conduit: Cables are pulled through protective conduits, offering additional protection against damage.
4. Backfilling
- Trenches are carefully backfilled with soil or other materials.
- Ensuring the ground is compacted and stable to prevent future subsidence or damage.
Depth Requirements
Residential depth standards (18-24 inches) protect cables from surface activities such as gardening and minor construction work. Deeper installations reduce the risk of accidental damage, ensuring long-term reliability.
Role of Easements and Road Rights-of-Way
Easements and road rights-of-way allow utility companies access to private land for installation and maintenance without infringing on property rights. These agreements, as outlined in detail here, are crucial for laying cables along roadsides and across private properties, ensuring seamless power supply distribution.
Example Scenario: Protek Electrical and Data
Protek Electrical and Data, a certified electrical company, is an excellent example of expertise in underground power line installation. In a new residential development:
- They conduct thorough site assessments and obtain necessary permits.
- Their skilled team uses advanced trenching equipment to minimize disruption.
- They choose optimal cable laying methods based on specific site requirements, ensuring robust installation.
- Finally, they complete backfilling meticulously, restoring the site while ensuring stability and safety.
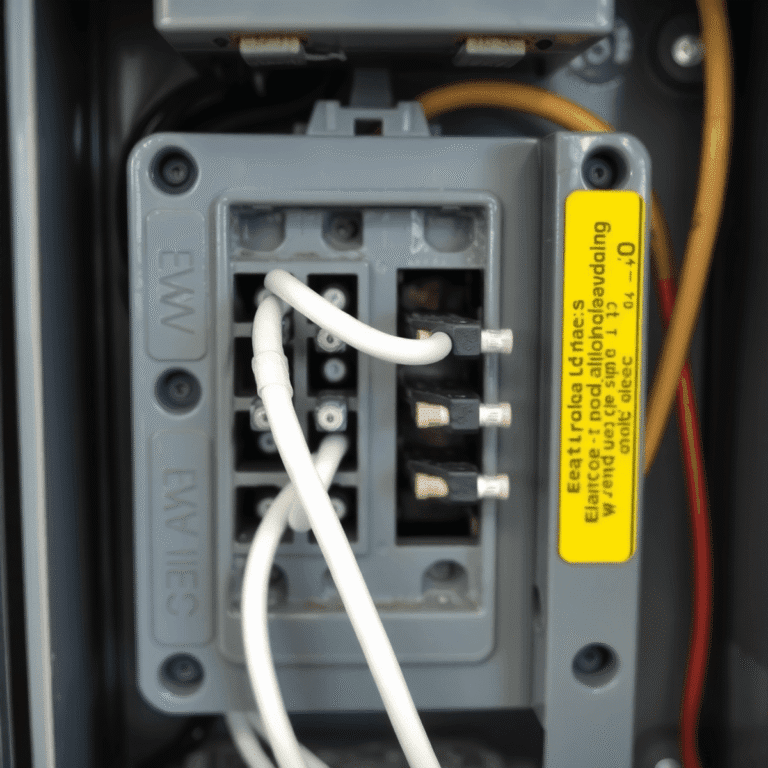
Materials Used in Underground Power Line Installation
Selecting the right underground cable materials is critical to both safety and longevity. Most underground power lines use insulated copper or aluminum cables. Copper delivers excellent conductivity and durability, while aluminum offers a lighter, more cost-effective option for longer runs. Both types are heavily insulated to withstand moisture, chemicals, and soil movement.
Protective Conduits
Protective conduits play a key role in preventing accidental damage. Rigid PVC or HDPE (high-density polyethylene) conduits are commonly used to encase cables, shielding them from shifting soil, water ingress, rodents, and mechanical impact. In high-risk zones—such as driveways or areas with frequent digging—reinforced steel conduits add another level of protection.
Trenching Equipment
Trenching equipment has evolved to minimize landscape disruption. Directional boring machines allow installers to run cables beneath roads or established landscaping without extensive excavation. Trenchers with precision controls ensure cable depth standards are met while leaving the smallest possible footprint.
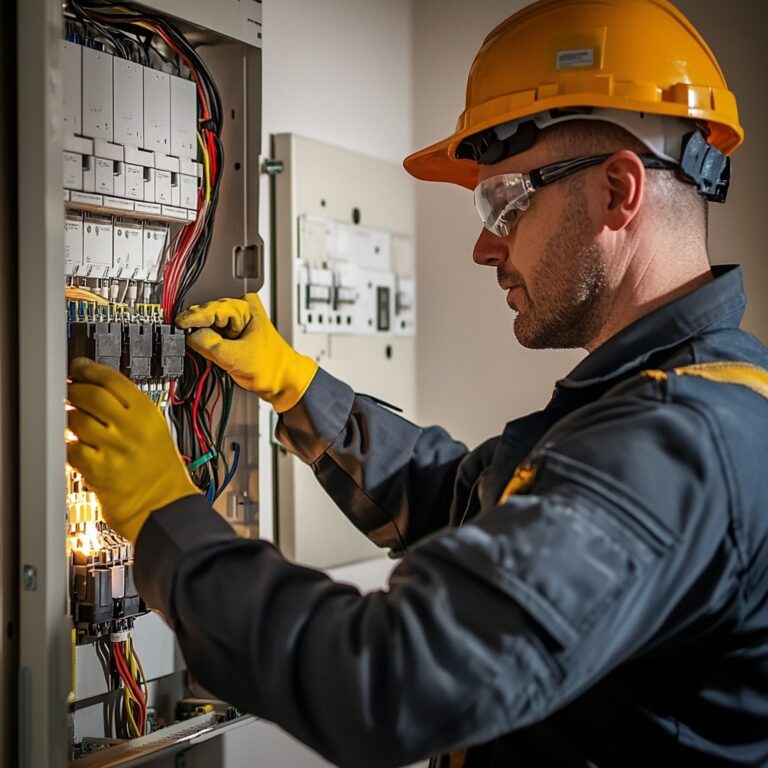
Safety Measures
Safety on site remains paramount during installation. Crews utilize insulated tools and lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization. High-visibility barriers keep residents and passersby away from open trenches. Soil is tested for contaminants before digging begins, and all workers wear appropriate PPE (personal protective equipment) including helmets, gloves, and safety boots.
Understanding how underground power lines are installed and maintained starts with knowledge of these essential materials and technologies. For example, the use of specific materials and methods in underground utility construction can significantly influence the outcome of such projects. The right combination ensures reliable electricity delivery with minimal risk to people or infrastructure.
Benefits vs Challenges: A Balanced View on Underground Power Lines
When comparing the underground power line benefits to traditional overhead wiring, several distinct advantages stand out:
- Reduced Outages: Underground lines are shielded from wind, wildfires, and accidental vehicle collisions. This protection translates into fewer service interruptions during storms or emergencies.
- Enhanced Visual Appeal: Neighborhoods with buried cables enjoy uncluttered skies and improved streetscapes. The absence of poles and wires creates a cleaner, modern look that often increases property value.
- Increased Safety: With wiring placed below ground, risks from downed live wires are virtually eliminated. Children, pets, and residents face fewer electrical hazards compared to areas with overhead lines.
Despite these strengths, the challenges of underground wiring should not be overlooked:
- Higher Initial Costs: Installing underground systems typically costs three to five times more per foot than overhead alternatives. The need for specialized equipment, materials, and labor all contribute to this premium.
- Environmental Vulnerabilities: While safe from wind and fire, underground lines are at risk during flooding or seismic events. Water intrusion can cause extensive damage, requiring complex repairs.
- Repair Complexity: Faults in buried cables demand excavation and advanced diagnostics. Repairs take longer and may disrupt nearby infrastructure or landscaping.
The balance between reliability, safety, aesthetics, and cost determines whether an underground system is the right fit for each project. Exploring how these factors influence ongoing maintenance highlights key considerations for property owners and utilities alike.
Maintaining Underground Power Lines: What You Need to Know
Routine maintenance on underground power lines is minimal compared to overhead systems. The primary reason is the cables’ protection from wind, storms, tree branches, and wildlife. Shielded by earth and conduit, these lines face fewer day-to-day hazards—leading to lower rates of routine inspections and repairs.
When faults do occur, the situation changes dramatically. Fault detection in underground cables requires specialized equipment such as time-domain reflectometers or cable fault locators. Unlike overhead wires where visual cues often reveal the problem, locating a break or short in a buried line is rarely straightforward. Once detected, the repair process for underground lines typically includes:
- Pinpointing the fault location using diagnostic tools
- Excavating the affected section—often disrupting landscaping or paved surfaces
- Replacing or splicing cables within protective conduits
- Restoring the site after repairs are completed
The repair process for underground lines generally costs more and takes longer than overhead repairs due to excavation requirements and limited visual access.
Utility companies schedule regular inspections using advanced diagnostics—infrared imaging, partial discharge testing, and cable insulation monitoring—especially before planned outages or upgrades. These proactive steps help reduce unexpected failures and keep maintenance efficient without unnecessary disruption to service.
Regular monitoring and prompt response are essential for ensuring reliability when faults do arise in underground networks.
Staying Safe Around Underground Power Lines
Ensuring safety around underground power lines is crucial. Contacting “Call Before You Dig” or private utility locators before any excavation on private property is essential to avoid damaging buried utilities. These services will mark the locations of underground cables, pipes, and other utilities, preventing accidental disruptions and potential hazards.
Building structures close to or directly over buried power lines presents significant risks:
- Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Concerns: Proximity to underground power lines can raise concerns about electromagnetic fields. Although most residential underground lines are well-shielded, it’s important to consider EMF exposure, especially in sensitive areas like schools or healthcare facilities.
- Restricted Maintenance Access: Structures built over or near buried power lines can severely restrict access for maintenance and emergency repairs. This could lead to increased costs and delays in addressing faults or upgrades.
Staying informed and cautious about the presence of underground power lines ensures not only the safety of your property but also the reliability of your electrical supply.
Case Study: Protek Electrical and Data’s Approach to Underground Installations
Protek Electrical and Data installations stand out across Melbourne’s western suburbs. With over 15 years of hands-on experience, their team delivers underground power line solutions tailored for commercial and industrial environments. Every project starts with a thorough site assessment, ensuring the correct selection of cables, conduits, and protective measures.
Key elements of their approach include:
- Meticulous Workmanship: Each installation is executed with precision, minimizing disruption and preserving site integrity through careful trenching and cable laying.
- Strict Safety Protocols: Certified electricians adhere to rigorous safety standards at every stage—protecting both workers and property owners from electrical hazards.
- Customer Focus: Clients benefit from clear communication, upfront menu-based pricing, and a commitment to exceeding expectations with neatness, reliability, and long-term performance.
Protek Electrical Data installations reflect a reputation built on quality service, trustworthiness, and consistent satisfaction in the field of underground power line infrastructure. Their expertise ensures that each system is efficient, compliant, and future-ready.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Underground Power Line Installation and Maintenance
The future of underground power lines is changing quickly as utilities look for smarter, safer, and more affordable solutions. Here’s how things are evolving:
Smarter Decisions with Data Analytics
Data analytics now play a critical role in pinpointing which overhead lines should be prioritized for underground conversion. By analyzing various factors such as outage records, weather risks, population density, and infrastructure age, decision-makers can optimize investments and enhance reliability in high-impact zones.
Safer Maintenance with Smart Grid Technology
Integration with smart grid technology is transforming the maintenance landscape. Remote sensors embedded along underground networks allow for real-time monitoring and rapid fault detection—reducing the need for disruptive manual inspections. When anomalies like insulation breakdown or moisture ingress are detected, technicians receive instant alerts. This results in targeted maintenance responses, minimized downtime, and increased operational efficiency.
A Resilient Future for Urban Environments
As urban environments grow more complex and resilient infrastructure becomes a necessity, these innovations are shaping a future where underground power delivery is not just safer but also smarter and more responsive to evolving community needs.
Conclusion
Understanding How Underground Power Lines Are Installed and Maintained is essential for ensuring safe, reliable infrastructure in modern communities. Choosing certified professionals, such as the team at Protek Electrical and Data, guarantees not only expert installation and repairs but also peace of mind through strict adherence to safety standards and quality workmanship. For any underground power project—residential, commercial, or industrial—you benefit most from working with a trusted provider dedicated to customer satisfaction and long-term reliability.
Summary underground power lines installation maintenance: Invest in professional expertise to safeguard your property, optimize performance, and ensure safe operation for years to come.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are underground power lines and why are they becoming more important?
Underground power lines are electrical cables installed below the ground surface, offering a reliable alternative to traditional overhead lines. Their growing importance stems from benefits such as enhanced safety, improved aesthetics, and increased protection from weather-related disruptions.
How is the installation process of underground power lines carried out?
The installation involves careful planning, trench digging at typical depths of 18-24 inches for residential areas, laying insulated copper or aluminum cables either by direct burial or within protective conduits, and backfilling. Easements and road rights-of-way play crucial roles in determining installation locations. Certified companies like Protek Electrical and Data specialize in these installations.
What materials and safety measures are used during underground power line installation?
Installation uses insulated copper or aluminum cables protected by durable conduits to prevent damage. Advanced trenching equipment minimizes disruption, while strict safety protocols protect both workers and nearby residents throughout the process.
What are the main benefits and challenges associated with underground power lines?
Benefits include reduced outages caused by wind, wildfires, or vehicle collisions; improved neighborhood aesthetics; and enhanced safety from electrical hazards. Challenges involve vulnerability to flooding and earthquakes, as well as higher initial costs—typically three to five times more expensive per foot compared to overhead lines.
How are underground power lines maintained and repaired?
Routine maintenance is generally lower due to protection from weather exposure. However, faults can be complex to detect and often require excavation for repairs, making them more costly and time-consuming than overhead line repairs. Utility companies perform regular inspections using advanced diagnostics before planned outages for repairs or upgrades.
What safety precautions should be taken around underground power lines?
It is essential to contact services like ‘Call Before You Dig’ or private utility locators before any excavation on private property to avoid damaging buried utilities. Additionally, building structures close to or over buried power lines poses risks including electromagnetic field exposure and restricted access for maintenance.