How Electricians Trace a Fault in a Hidden Cable
The Importance of Fault Tracing in Hidden Cables
Hidden cables run behind walls, under floors, or above ceilings—out of sight but essential for powering homes and businesses. These concealed wires are common in both residential and commercial settings, installed to maintain a tidy appearance and protect cables from physical damage. Despite these advantages, hidden cabling is still vulnerable to faults. Moisture ingress, accidental drilling, rodent activity, or simple wear and tear can all lead to issues like short circuits or open circuits.
Accurate fault tracing is critical for electricians. When a problem arises in a hidden cable, guessing the fault location leads to unnecessary holes in walls or floors—wasting time and driving up costs. Precise techniques allow electricians to pinpoint faults quickly and safely. This minimizes disruption to your property while ensuring that underlying electrical issues are addressed without delay.
Key takeaway:
Efficient fault tracing methods used by skilled electricians not only prevent excessive damage to building structures but also reduce the time needed for repairs. You benefit from restored power with less mess, lower labour costs, and peace of mind knowing the repair meets safety standards.
Knowing how electricians trace a fault in a hidden cable is fundamental for anyone who values safety, cost control, and property integrity. If you find yourself in need of professional assistance for such issues, consider reaching out to Proteked, experts in fault tracing and repair.
Techniques Used by Electricians to Trace Faults in Hidden Cables
1. Visual Tracing and Non-Invasive Techniques
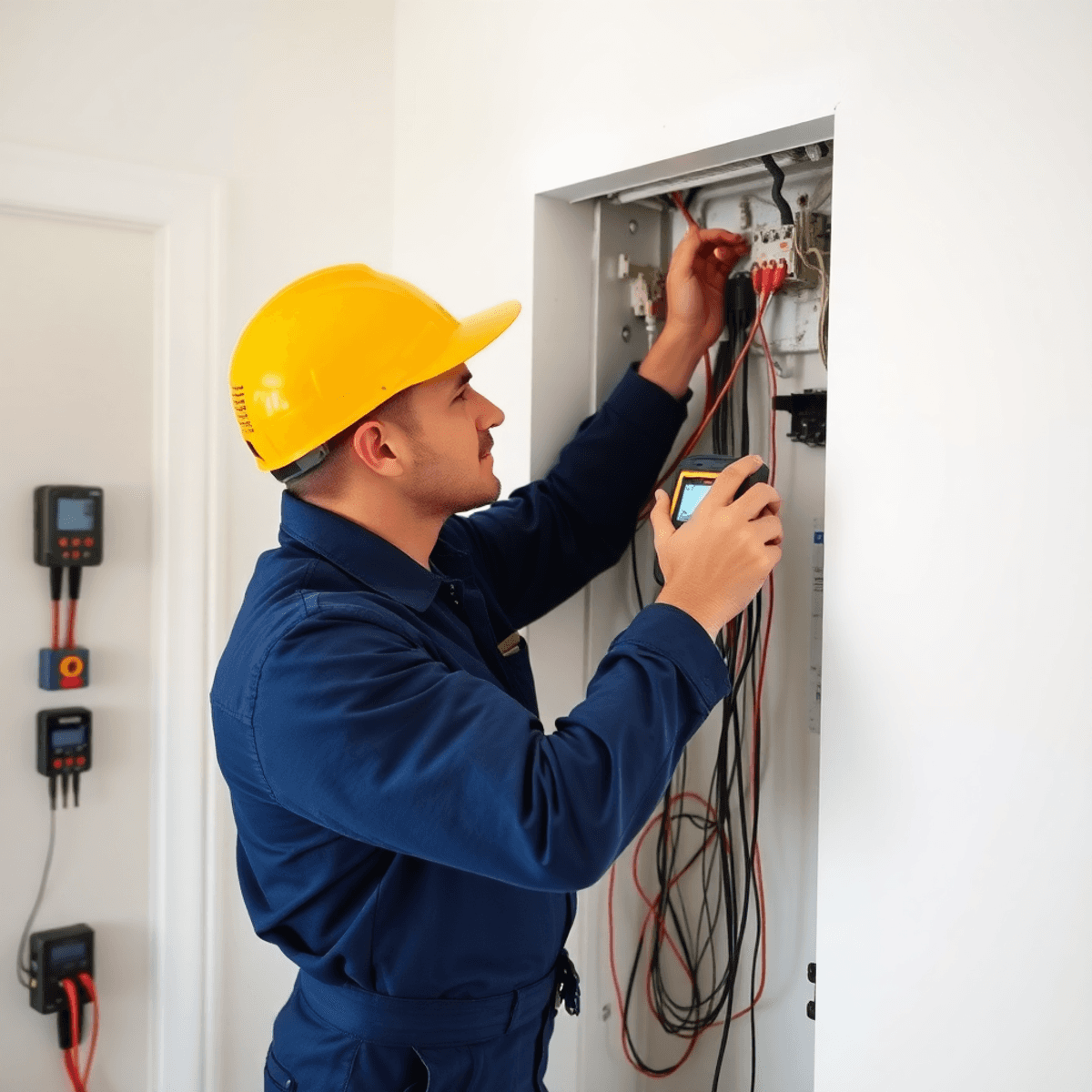
Hidden cables create a unique challenge for fault detection, especially in modern buildings where much of the wiring is concealed behind walls, ceilings, or floors. Experienced electricians rely on a combination of visual tracing and non-invasive techniques to pinpoint faults with accuracy—often without the need for disruptive demolition.
Locating Wires Through Outlets and Appliances
- Outlets, switches, and fixed appliances act as accessible points for tracing circuits.
- By systematically removing outlet covers or switch plates, electricians can visually inspect connections for signs of wear, overheating, or loose wires—common culprits behind hidden cable faults.
- Skilled technicians often follow wiring runs from one outlet to another, mapping how power flows through the property. This hands-on approach narrows down potential fault locations before any sophisticated tools are brought in.
- In commercial environments with complex panel boards or control systems, visual inspection around terminal blocks and junction boxes helps identify issues such as corrosion or improper terminations.
Using Stud Finders to Detect Wires Behind Walls
- Modern stud finders do more than locate timber framing—they can detect electrical wiring embedded within plasterboard or masonry.
- Advanced models use sensors that react to changes in density and electromagnetic fields caused by metallic wires.
- By running the stud finder along the wall’s surface, electricians can trace cable paths accurately while minimizing unnecessary wall damage.
- Some professional-grade devices include live wire detection features that alert users if the tool passes over energized cables—a critical safety advantage.
Utilizing Voltage Detectors to Identify Live Wires Without Invasive Methods
- Non-contact voltage detectors allow electricians to safely check whether a cable is live without stripping insulation or opening up walls.
- These handheld devices emit an audible beep or visual signal when held near an energized conductor, making them invaluable for quick verification during troubleshooting.
- Voltage detectors are especially useful when checking multiple outlets on a single circuit. Electricians can rapidly identify which segments are receiving power and which are not—helping to localize a break or fault point in hidden wiring runs.
- For high-density environments like apartment complexes or office spaces, non-invasive voltage detection becomes essential for both speed and safety.
Key takeaway:
Visual tracing and non-invasive techniques set the foundation for efficient fault detection. By leveraging accessible outlets, modern stud finders, and non-contact voltage detectors, professionals minimize disruption while maximizing diagnostic precision.
Electricians equipped with these methods consistently deliver safer repairs and avoid unnecessary wall destruction. The ability to trace hidden faults with minimal impact on property is a hallmark of skilled workmanship—essential for both residential projects and large-scale commercial maintenance.
2. Specialized Tools for Tracing Hidden Cable Faults
Electricians often rely on specialized tools to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of tracing faults in hidden cables. These tools are designed to locate and diagnose issues with both energized and de-energized cables.
1. Tone Generators
- Functionality: Tone generators are essential for fault detection in hidden cables. They work by sending a specific signal through the wire, which can then be detected using a compatible receiver.
- Application: By attaching the tone generator to one end of the cable, electricians can trace the signal along the length of the wire, helping them locate breaks, shorts, or other faults without invasive methods.
- Advantages: This method is particularly useful in complex wiring systems where visual tracing and non-invasive techniques might fall short.
2. Circuit/Wire Tracers
- Role: Circuit or wire tracers are versatile tools used to locate both energized and de-energized cables. They come with a transmitter and a receiver that help trace the path of electrical circuits.
- Operation: When connected to a circuit, the transmitter sends a signal that can be picked up by the receiver along the cable’s route. This allows electricians to pinpoint the exact location of faults or breaks.
- Utility: Wire tracers are invaluable in scenarios where cables run behind walls or underground, making visual inspection impractical.
3. Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)
- Overview: TDR devices offer high accuracy in fault identification by measuring reflections along a cable. The principle is similar to radar: a pulse is sent down the cable, and reflections from discontinuities (such as faults) are analyzed.
- Process: By analyzing these reflections, electricians can determine both the nature and location of faults with great precision.
- Benefits: TDR is particularly effective for identifying faults over long distances, making it ideal for commercial and industrial applications where extensive cabling is common.
Using these specialized tools ensures that electricians can swiftly and accurately identify faults within hidden cables. This minimizes disruption to walls and floors while significantly reducing repair time.
3. The Fault Location Process: Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively trace faults in hidden cables, electricians follow a systematic process that combines visual tracing and non-invasive techniques with advanced tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the fault identification process:
1. Identifying the General Area of a Cable Fault
- Visual Tracing: Begin by inspecting outlets and appliances connected to the suspected faulty circuit. Check for signs of damage or wear, such as burn marks or frayed wires.
- Non-Invasive Techniques: Use stud finders to detect wires behind walls. This helps pinpoint the approximate location of hidden cables without causing damage.
- Voltage Detectors: Utilize voltage detectors to identify live wires and ensure safety while working. This step is crucial for verifying which parts of the circuit are still energized.
2. Connecting a Tone Generator
- Attaching the Tone Generator: Connect a tone generator to one end of the cable or at an outlet on the faulty circuit. The tone generator sends a signal through the cable, making it easier to trace.
- Using a Probe: Follow the signal using a probe, which emits an audible tone when it detects the signal from the tone generator. Move along walls, floors, and ceilings, listening for changes in the tone to locate breaks or faults in the cable.
- Marking Fault Locations: Once you identify where the signal is lost or significantly weakened, mark these locations for further inspection or repair.
This methodical approach ensures precise fault detection while minimizing unnecessary damage to walls and floors. By combining traditional and modern techniques, electricians can efficiently locate and address hidden cable faults, ensuring safe and effective repairs.
4. Safety Measures, Best Practices, and Local Codes Compliance
Electrical fault detection—especially when dealing with hidden cables—demands strict adherence to safety protocols. Certified professionals prioritize safety not just for themselves but for property owners and occupants as well.
Essential Safety Steps:
-
Power Isolation:
Before any cable tracing, fault detection, or visual tracing takes place, the power supply to the relevant circuit must be switched off at the breaker. This eliminates the risk of electric shock or equipment damage during inspection or repair. -
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Electricians wear insulated gloves and rated eye protection when working around outlets and appliances, behind walls, or near ceiling spaces. PPE is non-negotiable when using stud finders, voltage detectors, or performing non-invasive techniques that involve close proximity to electrical infrastructure. -
Tool Inspection:
Regular checks ensure that voltage detectors, stud finders, tone generators, and other diagnostic devices are in proper working condition. Damaged leads or faulty tools can compromise both accuracy and safety. -
Safe Access Practices:
When gaining access to hidden wiring—whether by removing outlet covers or making small inspection holes—electricians avoid unnecessary disruption to walls and floors. The use of non-invasive techniques limits exposure to sharp tools and reduces the risk of accidental contact with live conductors. -
Compliance With Local Codes:
Every step in the fault location process aligns with Australian Standards (such as AS/NZS 3000) and local council regulations. This guarantees not only effective repairs but also long-term safety and insurance compliance for property owners.
Professional electricians never cut corners with safety. Each method—from traditional visual tracing to advanced cable fault detection—incorporates best practices designed to protect both people and property.
Maintaining rigorous safety standards is foundational across all stages of locating faults in hidden cables. This approach builds trust with clients and ensures repairs meet both technical requirements and regulatory obligations.
Conclusion
Effective fault tracing methods are crucial for both electricians and property owners. Accurate identification of faults in hidden cables ensures safe and efficient repairs while minimizing damage to walls and floors. By using efficient fault tracing techniques, electricians can significantly reduce repair time, ultimately saving costs and preventing potential hazards.
Understanding how electricians trace a fault in a hidden cable provides property owners with insight into the complex process and the importance of hiring skilled professionals. With proper tools, techniques, and adherence to safety protocols, electricians can deliver high-quality service that guarantees customer satisfaction and trust-building through exceptional workmanship.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are hidden cables and why do they develop faults?
Hidden cables are electrical wires concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings. They can develop faults due to wear and tear, accidental damage during renovations, or environmental factors, making accurate fault tracing essential for safe repairs.
Why is fault tracing in hidden cables important?
Fault tracing in hidden cables is crucial for ensuring safety, minimizing damage to property, reducing repair time, and enabling efficient and precise repairs without unnecessary wall or floor destruction.
What non-invasive techniques do electricians use to trace faults in hidden cables?
Electricians use visual tracing through outlets and appliances, stud finders to detect wires behind walls, and voltage detectors to identify live wires without invasive methods, which help locate faults safely and efficiently.
Which specialized tools assist electricians in locating faults in hidden cables?
Specialized tools include tone generators that send signals through cables to detect faults, wire tracers for locating energized or de-energized cables, and Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) devices for accurate fault identification.
What are the typical steps involved in the fault location process for hidden cables?
The process involves identifying the general area of the cable fault using visual and non-invasive techniques, connecting a tone generator to the faulty cable to trace its path accurately, and then pinpointing the exact fault location for repair.
What safety measures should be observed when tracing faults in hidden cables?
Safety measures include turning off power before testing or cutting into walls, wearing protective gear such as gloves and eye protection when accessing wiring spaces, and adhering to local codes and best practices to prevent accidents.